Stem Cell therapy for COPD
and Pulmonary Emphysema
Stem cell therapy for COPD, which includes chronic bronchitis and emphysema, improves breathing, restores blood flow to the lungs, and supports damaged tissue healing and repair.

Stem cell therapy is a minimally invasive, outpatient procedure with little to no recovery or down time

Before stem cell therapy is performed, the prospective patient must be evaluated by Stemwell’s medical team to determine if they are a candidate to be invited for treatment. Before proceeding with stem cell treatment for COPD, Stemwell’s doctors review the patient’s entire history, current lab results, and once in Bogota, a physical exam is completed.

The entire procedure takes three to five days in a clinical outpatient setting and requires little to no down time.
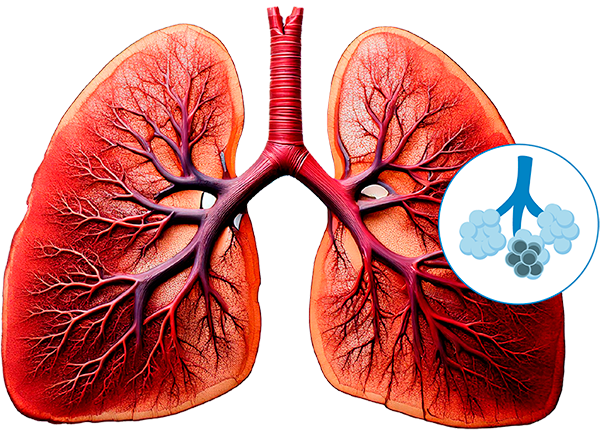
Emphysema, a form of COPD, is a long-term, progressive lung disease with symptoms including frequent coughing or wheezing, shortness of breath, especially with activity, mucus production, etc. With emphysema, the alveoli are damaged, causing them to eventually rupture.
This creates one large air space instead of many small ones and reduces the available area for gas exchange. Because blood oxygenates inside the alveoli, the amount of oxygen that reaches the bloodstream is reduced.
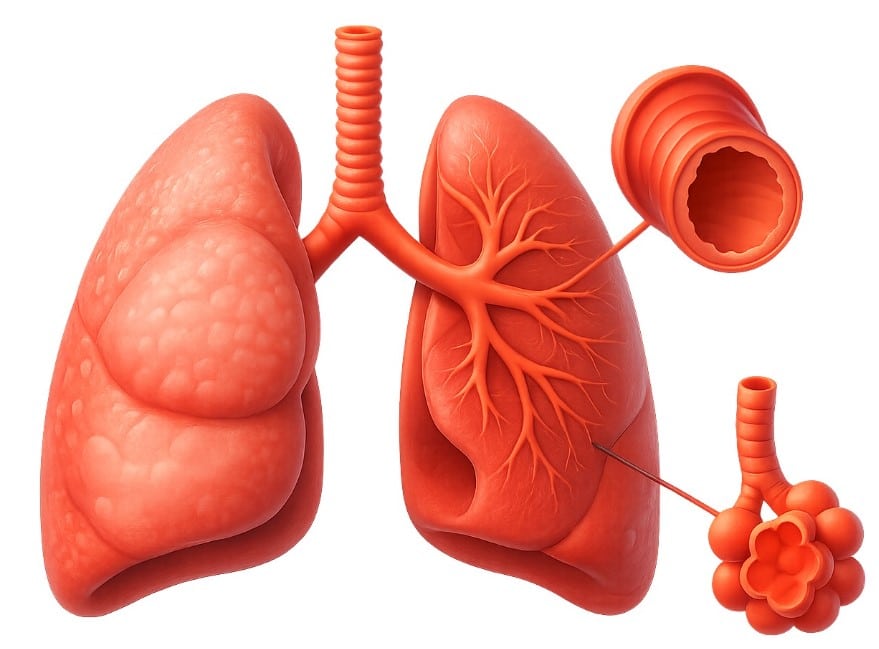
COPD symptoms frequently do not appear until significant lung damage has occurred, and they typically worsen over time, especially if the patient is a smoker.

People with mild COPD (stage 1) have a good prognosis and may have a relatively normal life expectancy, but this decreases as disease severity increases.

People with COPD who are admitted to an ICU may have up to a 24% mortality rate, which can double for people 65 years and older

A COPD patient who receives a lung transplant has a median survival of 5.2 years, provided that there are no further complications.
What is the science behind stem cell therapy for COPD and lung disease?
Stem cells have the potential to regenerate or repair damaged lung tissues and improve symptoms of COPD or lung disease. Stem cells are explored for their abilities in:
Reducing inflammation
Modulating the immune response

Secreting growth factors that may aid tissue repair.
The stem cells may integrate into lung tissues helping to restore functions and improve symptoms.

What is COPD?
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) is a progressive and long-term respiratory condition characterized by persistent inflammation and damage to the airways and lungs. This results in airflow obstruction, making it increasingly difficult to breathe. COPD often develops due to prolonged exposure to harmful irritants, such as cigarette smoke, environmental pollutants, or occupational hazards like chemical fumes and dust.
As COPD advances, lung function deteriorates, leading to worsened breathing difficulties and an increased risk of complications such as heart disease, lung cancer, and other chronic inflammatory conditions.

This disease significantly impacts quality of life, and without proper management, its progression can become debilitating.
The symptoms of COPD can vary in severity but generally include:
Wheezing
A whistling or squeaky sound when breathing.
Shortness of Breath (Dyspnea):
Difficulty breathing, especially during physical activities.
Chronic Cough:
A persistent cough that may produce mucus.
Excessive Mucus (Sputum) Production:
Thick mucus buildup in the lungs, often expelled during coughing.
Fatigue:
Ongoing tiredness and lack of energy due to limited oxygen levels-
Frequent Respiratory Infections:
Increased vulnerability to colds, pneumonia, and other lung infections.

COPD Exacerbations
People with COPD often experience episodes known as exacerbations, during which symptoms suddenly worsen and persist for several days. These flare-ups can be triggered by infections, exposure to irritants, or even changes in weather and stress, further damaging the lungs and impacting overall health.
Early diagnosis and effective management of COPD are crucial to slowing disease progression, improving breathing, and enhancing quality of life. Innovative therapies, including regenerative medicine, offer hope for restoring lung health, reducing inflammation, and minimizing exacerbations.
At ReGenesis, we focus on advanced treatments that target the root causes of COPD, providing a path toward better respiratory
The Effectiveness of Stem Cell Therapy for COPD and Pulmonary Emphysema
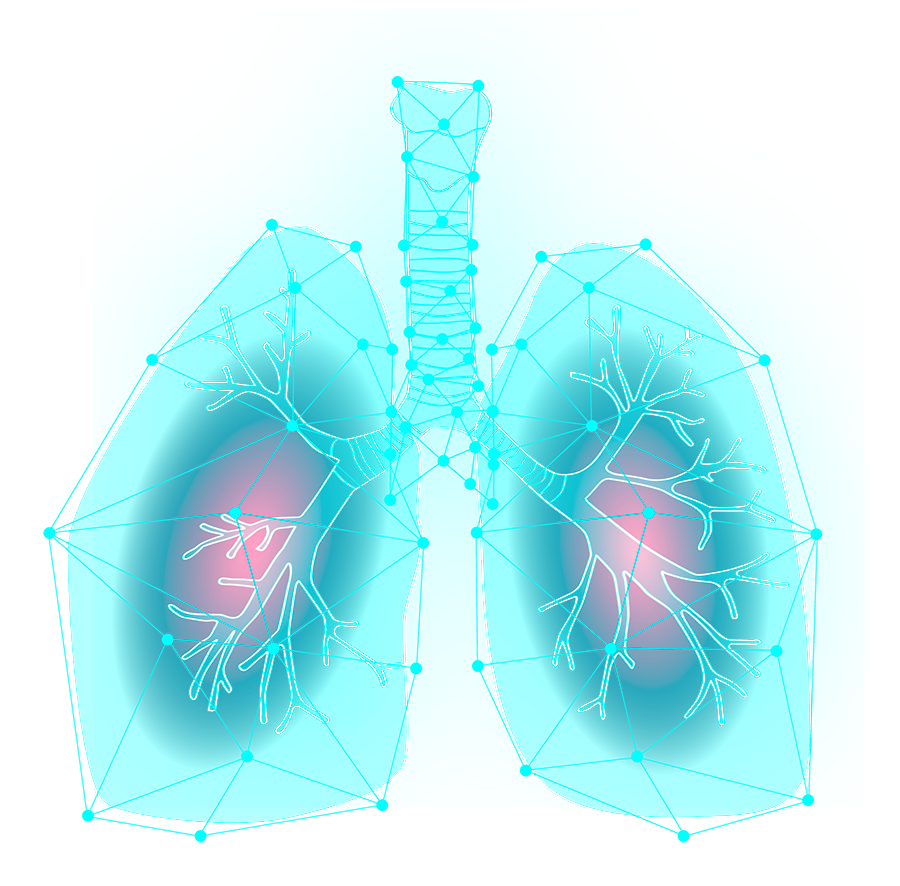
How Stem Cell Therapy Works for COPD
Stem cell therapy offers a promising, minimally invasive treatment for Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD), including conditions like chronic bronchitis and emphysema.
By harnessing the regenerative properties of stem cells, this therapy:

Improves breathing by enhancing lung function.
Restores blood flow to the lungs, supporting oxygenation.

Facilitates the repair and healing of damaged lung tissue
The procedure is conducted on an outpatient basis, requires minimal recovery time, and allows patients to resume their daily activities quickly.
Before undergoing stem cell therapy, patients are thoroughly assessed by ReGenesis' medical team to determine their suitability for treatment. This process includes:
A comprehensive review of the patient’s medical history.
Analysis of current lab results.
A physical examination conducted upon arrival at our clinic in Bogotá
The entire treatment protocol spans three to five days in a clinical outpatient setting, with little to no downtime required.
What is Pulmonary Emphysema?
Pulmonary emphysema, a form of COPD, is a progressive lung disease that damages the alveoli—the tiny air sacs responsible for oxygen exchange in the lungs. Over time, the alveoli rupture, reducing the surface area for gas exchange and limiting the amount of oxygen that reaches the bloodstream.
Symptoms of Pulmonary Emphysema Include:
Chronic coughing or wheezing

Shortness of breath, particularly during physical activity

Excessive mucus production
Symptoms often don’t manifest until significant lung damage has occurred, and they tend to worsen as the disease progresses, especially in smokers.
Mild COPD (Stage 1): Patients may have a relatively normal life expectancy with appropriate management.
Advanced COPD: Prognosis worsens as the disease progresses. ICU admission for COPD exacerbations carries a mortality rate of up to 24%, which doubles for patients aged 65 and older.
Lung Transplant: Patients who undergo a lung transplant have a median survival of 5.2 years, provided there are no major complications.
What is the science behind stem cell therapy for COPD and lung disease?
Stem cells have the potential to regenerate or repair damaged lung tissues and improve symptoms of COPD or lung disease. Stem cells are explored for their abilities in:
Reducing inflammation

Modulating the immune response
Secreting growth factors that may aid tissue repair
At ReGenesis, we are committed to delivering cutting-edge regenerative therapies tailored to address the root causes of lung disease, empowering patients to breathe easier and live better.